In rural regions within America, the social determinants of health have a significant impact on population health and typically contribute to poorer health among the communities than in more urban regions of America. Rural hospital closures widen the health care gap and exacerbate existing healthcare shortages.
Rural hospital closures affect access to healthcare
In rural areas, communities struggle to gain access to healthcare, leaving many people without the ability to obtain healthcare services in emergency situations, which can have lethal effects on the population. The US Department of Health and Human Services notes that there is no definition of “rural”; rather, rural areas are all areas that do not fall within the definition of “urban,” which includes 50,000 people or more.
The Texas Organization of Rural & Community Hospitals, however, defines a rural hospital as:
A hospital located in a county of 60,000 or fewer…a hospital in a Non-Metropolitan Statistical Area that is designated as a
- Critical Access Hospital,
- Sole Community Hospital, or
- Rural Referral Center.
There is no benchmark measurement or limit on the distance a patient must travel to reach the closest rural hospital.
Additionally, rural regions have a smaller proportion of residents with health insurance coverage, which makes it more challenging to afford vital healthcare services.
Since many primary care providers also offer services from a hospital setting, fewer patients can access primary care when hospitals close, increasing the danger from chronic conditions and adverse health risks for rural residents.

Dropstat’s features that support rural hospitals
For rural hospitals, insight into operations is one of the most critical aspects of ensuring reliable, accessible care to the community. But, to ensure that health care services can be delivered efficiently, rural hospitals must prioritize their workforce, not only in terms of nurse staffing levels but also costs associated with labor and effective processes to utilize staff effectively.
Dropstat’s integrated features include tools that support rural hospitals at risk of closing and rural healthcare in general:
- Cost tags: By using cost tags, your healthcare facility can compare the costs of different nurses within the same discipline to determine the most cost-efficient nurses. Healthcare facilities can give preference to less expensive staff, for example, to fill open shifts. This process reduces unnecessary labor costs and allows the facility to allocate unused funds for improving other hospital processes and services. Given that rural hospitals suffer from extreme financial loss as a result of labor costs, equipment, and supply costs, and low reimbursement rates, implementing methods such as cost-tagging to avoid extra expenses promotes more efficient use of funds.
- Overtime tags: Like cost tags, overtime tags help pinpoint specific nursing shifts that if a nurse would opt to schedule it for overtime, would put a nurse into overtime. The benefit of this feature is that it allows healthcare facilities to reallocate overtime shifts to staff members who would not be in overtime, ultimately reducing burnout among the workforce and saving on overtime costs.
- Retention programs: Rewards and retention programs aim to improve workplace culture by increasing motivation and recognition. This, in turn, reduces turnover, which saves on costs associated with recruitment, onboarding, and training.
- Agency oversight: Dropstat uses metrics such as cost of agency staff, number of agency staff from a specific discipline, and agency staff in overtime to give healthcare facilities the knowledge required to pinpoint holes in staffing practices and recurring shift shortages. This feature can help rural hospitals decrease the use of more expensive agency staff where appropriate. Saving on labor expenses, especially for rural hospitals, is a critical step in reducing unnecessary costs and preventing closure.
Dropstat’s integrated features are part of the digital transformation in healthcare, which assists healthcare facilities in gathering communication and economic insights.
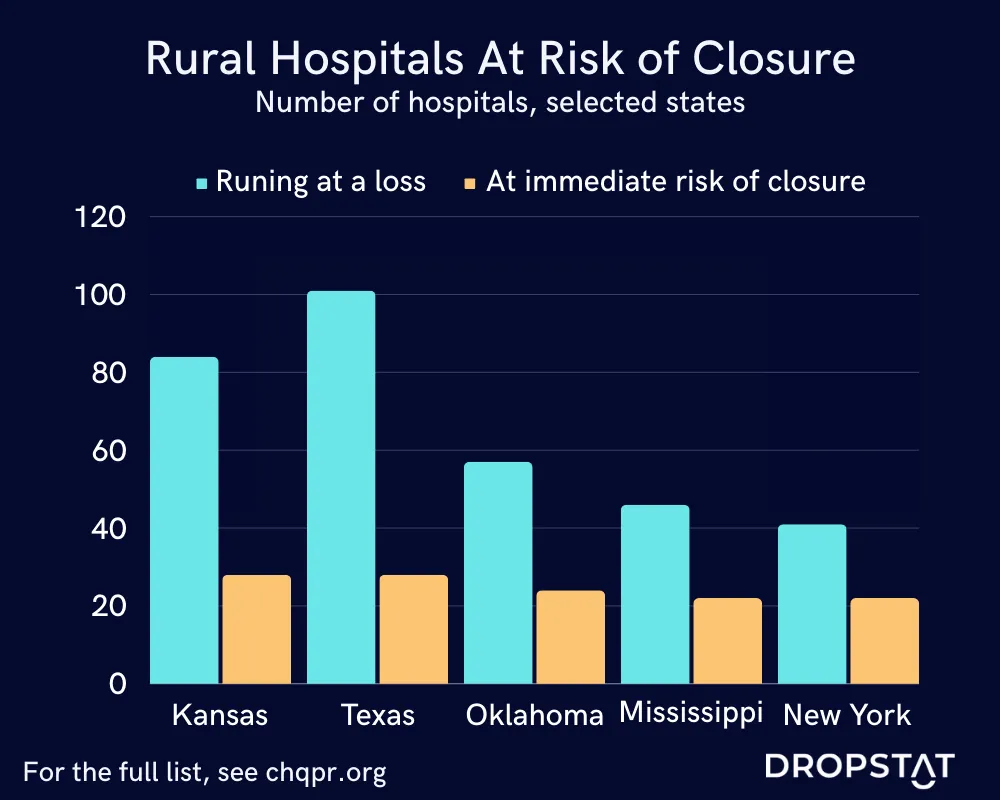
External and Internal Obstacles for Rural Hospitals
The American Hospital Association notes that some causes associated with hospitals closing include:
- Low health insurance reimbursement rates
- Rural hospitals experiencing low reimbursement rates are often unable to cover the cost of healthcare delivery. The lack of reimbursement is associated with public insurance plans, both Medicare and Medicaid, as well as private entities. The amount of bad debt accumulated from patients also contributes to the loss of revenue, leading to greater challenges in covering all hospital expenses.
- Healthcare staffing shortages
- While short staffing is a crisis that threatens healthcare institutions across the nation, rural hospitals closing may cause more severe consequences. Because primary care providers and specialty care providers are in low supply in many Health Professional Shortage Areas (HPSAs), patients are forced to travel further for their care, even in emergency situations. Additionally, the shortage of staff poses healthcare delivery risks as a result of unsafe labor loads leading to staff burnout and excessive overtime.
- Exaggerated labor costs
- Attracting and retaining staff to deliver health care services in rural communities is a difficult task as a result of a perceived lack of growth opportunities, feeling socially isolated, family considerations, and relocation. When facilities cannot fill their demand for staff, they often turn to staffing agencies and travel nurses to assist with filling shifts. A challenge to hospital finances alongside the staffing shortage, external labor costs pose another challenge for rural healthcare.
- Unique financial obstacles
- The COVID-19 pandemic has increased the cost of care in regard to personal protective equipment, drugs, and many other necessary healthcare products. The American Hospital Association notes that between 2019 and 2022, the cost of contract labor played a major role in the nearly 21% jump in the cost of labor. This is especially significant when we consider that the cost of labor is responsible for nearly half of a hospital’s expenses. Additionally, the median annual cost of a new drug is reported to be over $200,000. Similarly, higher costs for medical supplies and equipment lead to challenges in ensuring proper patient care and healthcare delivery.
- Inflexible governmental regulations
- Navigating cybersecurity requirements and HIPAA compliance presents many difficulties for rural hospitals since they have fewer resources to adapt to evolving protocols and technological advancements. One area that jeopardizes the financial security of rural hospitals is the increasing threat of data breaches. Difficulty with protecting patient information is caused by the limited budget that rural hospitals have for upgrading technology and software to protect from cyber-attacks and potential ransomware. Data breaches force hospitals to pay large sums to retrieve data.

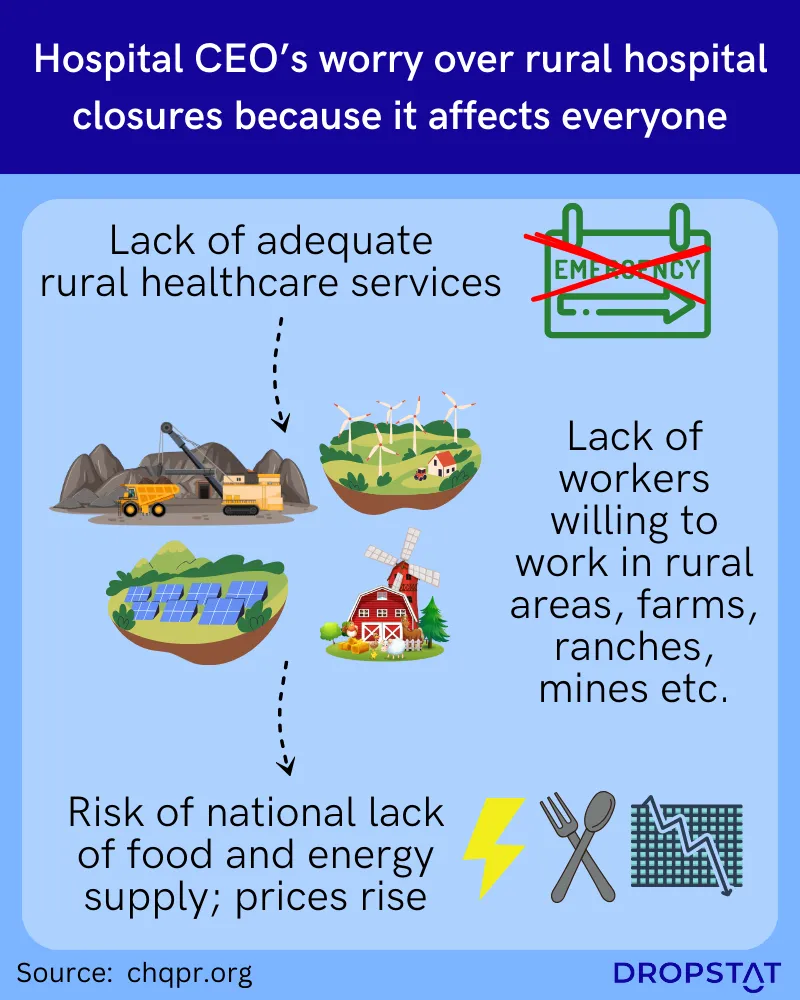
Rural Hospital Closures: Effects on Surrounding Communities
Closing hospitals increases the threat of poor population health and the inability to access healthcare when needed. The American Hospital Association reported that 136 rural hospitals shut down between 2010 and 2021, with the majority of the closures occurring in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
To put this into perspective, at the time of the 2010 U.S. Census, 60 million people were reported to be living in rural America. This gives us some idea of how many people are affected by compromised healthcare availability.
The ripple effect of these rural hospital closures on the surrounding communities is monumental.
- Affected communities have no choice but to travel significantly farther for both primary and specialty care. This is most problematic when seeking emergency services.
- Healthcare access barriers and hospital closures in rural counties are associated with fewer physicians and other healthcare providers. As a result of these closures, other healthcare facilities experience an increase in patient volume, potentially overwhelming their workforce and facility resources.
Rural Hospital Closures – Conclusion
The main challenges that rural hospitals face, such as low reimbursement, staffing shortages, financial obstacles, and governmental regulations, are causing rural hospitals to close, which has significant negative effects on the surrounding population. Such closures and a lack of sufficient healthcare delivery to serve the hospital’s catchment area potentially contribute to increasing rates of chronic disease and ripple effects that hit larger population service areas as people search for alternate healthcare facilities.
Rural healthcare facilities do have access to tools that could bring relief to some of the issues highlighted in this article.
How Dropstat can help avoid hospital closures by focusing on scheduling and expenditure
Many rural hospitals have closed because of financial and staffing obstacles; many more hospitals are threatened with closure. With intervention, however, rural hospital closures are not inevitable.
Dropsat’s advanced AI-powered staff scheduling app has helped many larger and smaller healthcare facilities regain control of their staffing expenditures and scheduling challenges.
Schedule a demo with Dropstat today to learn more about how Dropstat can help your rural hospital reduce staffing expenses and improve scheduling issues.







