Dropstat’s Clickable Guide to Types of Nursing Specialties
Healthcare leaders can gain valuable insights into understanding and improving the nursing hierarchy to foster a safer and more positive environment. Understanding the nurse hierarchy is essential for effective leadership and resource management in healthcare facilities.
What is a hierarchy in healthcare?
In healthcare, a hierarchy refers to the systematic arrangement of roles and responsibilities among healthcare professionals based on their authority and level of expertise and qualifications. It provides a framework that outlines the organization’s reporting relationships and decision-making processes.
What is the nursing hierarchy?
The nursing hierarchy outlines the different levels of nursing expertise and responsibility within the nursing profession. The hierarchy of nurses focuses on the roles and responsibilities of nurses. A hierarchy establishes the orderliness of authority and leadership within a profession. In nursing, the range of nurses goes from frontline nurses and nursing assistants all the way up to nurse managers and nursing executives. It takes into account nurses’ skills and responsibilities, education, and licensing requirements.
The level of nurses in a healthcare facility directly impacts the delivery of patient care. The different levels are shown in the chart.
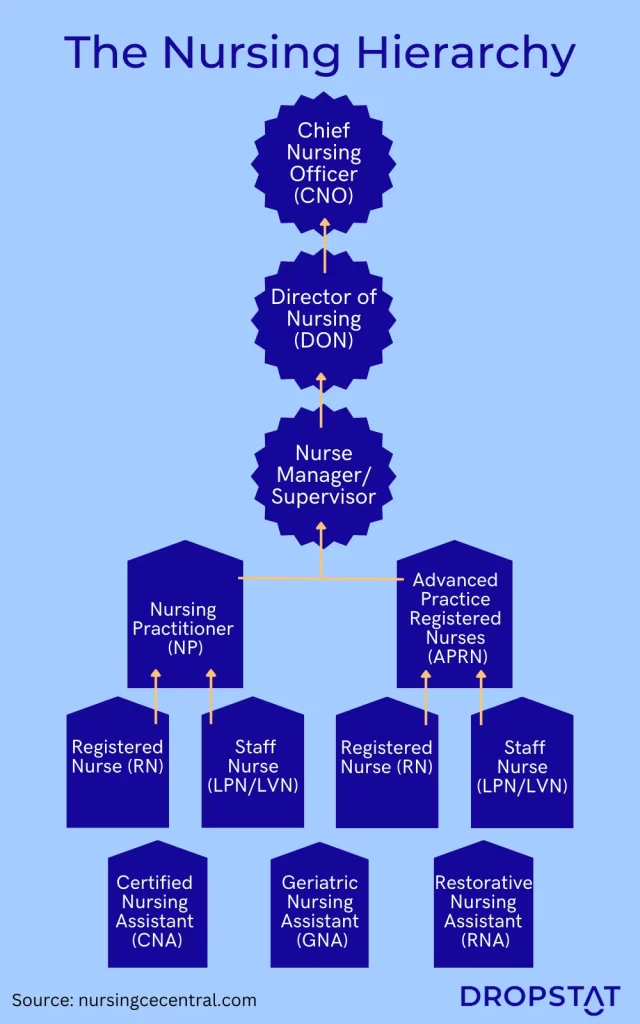
What are the levels of nursing from lowest to highest?
There are 3 categories in the nursing hierarchy, entry-level, advanced-level, and senior-level nursing.
Level 1: Entry level
- CNA – Certified nursing assistant
- GNA – Geriatric nursing assistant
- RNA – Registered or rehabilitative nurse
- LNA – Licensed nursing assistant
- LPN – licensed practical nurses
- LVN – Licensed vocational nurses
- Care assistants
Level 2: Advanced level
- RN – Registered nurse – usually nurse managers
- NP – nurse practitioners
- APRN – Advanced practice registered nurses
- CNM – Certified Nurse Midwife
- CNS – Clinical Nurse Specialist
- CRNA – Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist
Level 3: Senior level
- CNO – Chief nursing officer – strategic leadership, oversees nursing operations
- DNP – Doctor of Nursing Practice
- Ph.D. in Nursing – Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing – research, nursing education, advanced clinical practice
Nurses at the highest level of care are involved in making decisions about ways to improve the delivery of care.
Some categorize nurses into non-degree, degree, and advanced degree nurses.

What is the significance of nursing hierarchy in hospitals?
It is crucial to have a nursing hierarchy in a hospital. The hierarchy helps all the nursing disciplines work together in the most efficient and effective way. You could compare it to an orchestra – each musician plays their designated instrument for the perfect musical blend.
The concept of nurse hierarchy in a hospital supports better
- collaboration
- communication
- coordination
- accountability
- decision-making
The nursing hierarchy ensures
- that responsibilities are appropriately delegated
- expertise is utilized most effectively
- nursing staff are supported in their professional growth and development.
The effect of hospital nurse hierarchy is demonstrated best when staff work agreeably in the appropriate tier of the hierarchy, and there is excellent collaboration.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of hierarchy in healthcare?
5 advantages of hierarchy in healthcare
1. Clear decision-making
A well-defined hierarchy in healthcare facilitates efficient decision-making processes. It provides healthcare staff with a structured framework where roles and responsibilities are clearly delineated, enabling faster and more effective decision-making to address patient needs and ensure timely interventions.
2. Specialization and expertise
A hierarchy allows for specialization and utilization of expertise within healthcare teams. Different levels of healthcare professionals, such as nurses, physicians, and specialists, bring their knowledge and skills to patients, who receive the appropriate level of care from professionals with expertise.
3. Efficient coordination
A hierarchical structure promotes efficient coordination and task allocation. By having designated roles and reporting relationships, healthcare teams can work cohesively, leveraging each member’s strengths and skills. This is essential for a smooth workflow, streamlined patient-care processes, and the most efficient utilization of resources.
3. Financial savings
Having a structured hierarchy makes financial sense for a healthcare facility owner. The gains are:
- Improved operational efficiency – for example, maintaining the number of RNs working in a facility with other supporting staff leads to long-term cost savings and profitability.
- Hiring enough of each level of nurse – without hiring overqualified, expensive staff to meet the nursing hours per patient day requirements (NHPPD) and safe staffing ratios.
4. Workplace culture
An effective hierarchy fosters a supportive workplace culture. It provides opportunities for
- professional growth
- mentorship
- career advancement
to promote job satisfaction and engagement among healthcare professionals.
5. Patient safety
A well-designed hierarchy in healthcare significantly contributes to patient safety and positive patient outcomes. Preset care protocols for designated staff reduce the risk of medical errors and adverse events.
Disadvantages of hierarchy in healthcare
1. Communication barriers
A hierarchical structure can create communication barriers within healthcare teams. The top-down flow of information may hinder effective information sharing and feedback from frontline staff, such as CNAs and LPNs, potentially impeding innovation, problem-solving, and the identification of areas for improvement, for example, regarding the nursing care plans that an RN wrote.
2. Limited autonomy
In a rigid hierarchy, healthcare professionals at lower levels may have limited autonomy and decision-making authority, leading to reduced engagement and job satisfaction. This can result in missed opportunities for leveraging their expertise, creativity, and critical thinking skills. This could stop nurses from advancing their skills and career plans.
3. Hierarchical culture
A damaging hierarchy in healthcare can perpetuate an environment of power dynamics, where the authority of higher-ranking individuals is unquestioned and unquestionable. Lower-level staff may feel disempowered or undervalued. A negative culture can negatively impact morale, teamwork, and collaboration, ultimately affecting patient care quality and outcomes.

Consequences of a damaging hierarchy in healthcare
A damaging hierarchy in healthcare can have severe consequences for patient safety and the workplace culture. Here are some ways in which a negative nursing hierarchy can pose risks:
- Lack of psychological safety: In a damaging hierarchy, there may be a culture of fear, intimidation, and reluctance to speak up. This hinders open communication in nursing and prevents healthcare professionals from raising concerns or reporting errors, ultimately compromising patient safety.
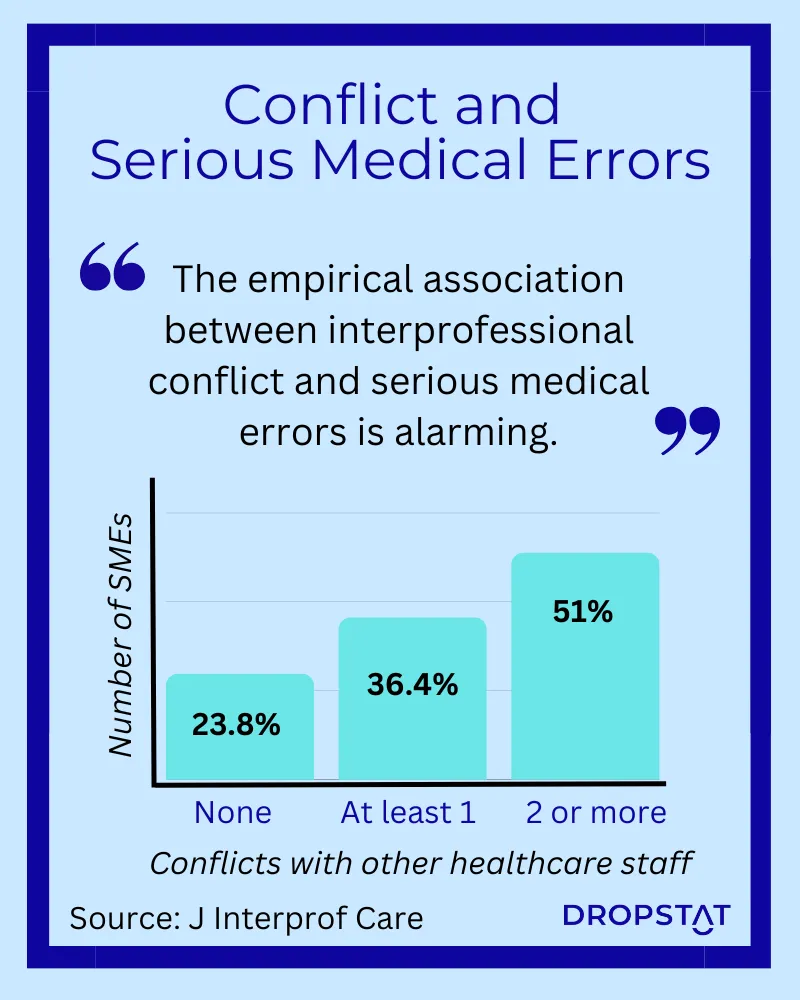
- Information bottlenecks: A rigid hierarchy can create information bottlenecks, where critical information fails to reach the right people at the right time. This can lead to delays in decision-making, inadequate coordination, and an increased risk of medical errors or adverse events.
- Limited collaboration and innovation: A damaging hierarchy may discourage collaboration and inhibit innovation. Healthcare professionals feel disempowered or undervalued and are less likely to contribute their ideas, insights, or best practices, hindering the organization’s ability to adapt, improve, and provide optimal patient care.
- Ineffective resource allocation: A hierarchical structure that does not take into account the expertise and insights of frontline staff can result in inefficient resource allocation. Higher-level decisions made without input from those directly involved in patient care may lead to ineffective utilization of resources, including staffing, equipment, and supplies.
- Reduced staff engagement and burnout: A damaging nursing hierarchy can contribute to increased levels of stress, burnout, and job dissatisfaction among healthcare professionals. This can have a detrimental impact on the overall workplace culture, leading to high turnover rates, compromised quality of care, and decreased patient satisfaction. Nurse bullying is an example of stress due to a negative nursing hierarchy.
Addressing a damaging hierarchy requires a commitment to change and a shift towards a more collaborative work culture. It involves fostering a culture of psychological safety, encouraging open communication, and empowering frontline staff to participate actively in decision-making and quality-improvement initiatives. By creating an environment that values teamwork, transparency, and continuous learning, healthcare organizations can improve patient safety, enhance workplace culture, and ultimately deliver better outcomes for patients and healthcare professionals.
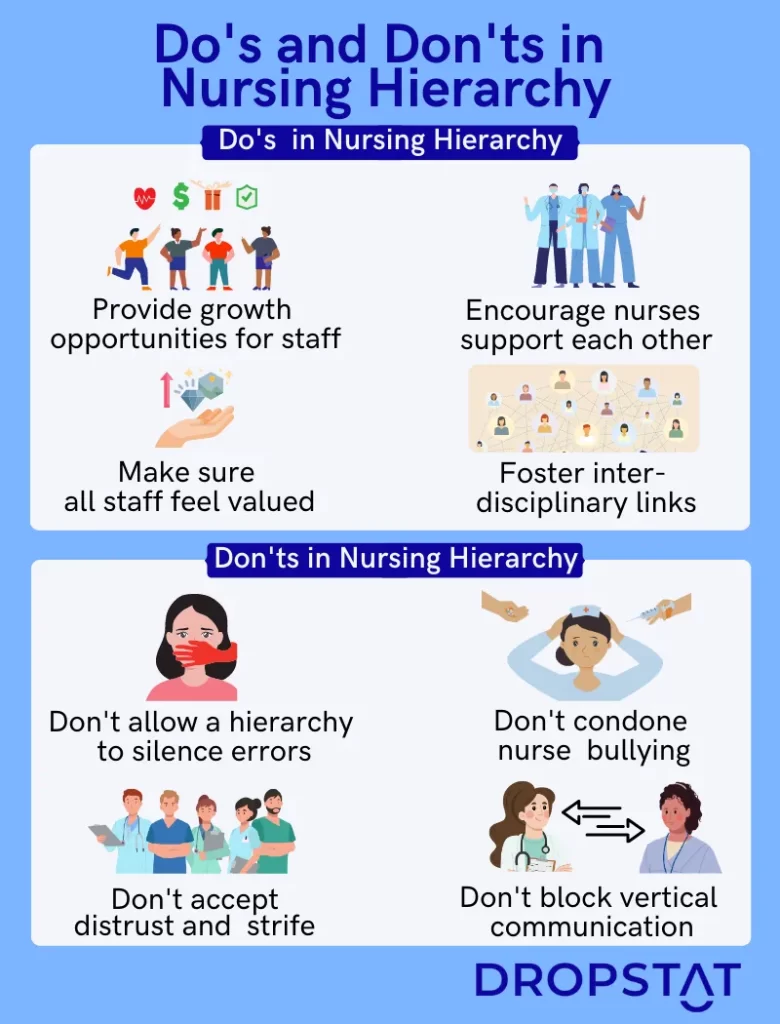
8 ways to optimize the nursing hierarchy in your facility
- Foster open communication: Build a culture where open and honest communication from nurses at all levels of the hierarchy is encouraged and valued. Establish channels for nurses to express their ideas, concerns, and feedback without fear of retribution.
- Empower frontline nurses: Recognize the expertise and knowledge of frontline nurses and involve them in decision-making processes. Provide them with autonomy and authority to make clinical judgments and implement evidence-based practices as permitted by their qualifications.
- Promote continuous education and professional development: Support nurses in pursuing ongoing education and professional growth. Offer opportunities for nurses to attend conferences, workshops, and training programs to enhance their knowledge and skills.
- Create and support mentorship programs: Establish mentorship programs where experienced nurses can guide and support less experienced colleagues. This allows for transferring knowledge, skills, and best practices, fostering a culture of learning and growth.
- Emphasize interdisciplinary collaboration: Encourage collaboration and teamwork among healthcare professionals from different disciplines. Create opportunities for nurses to work closely with physicians, pharmacists, therapists, and other healthcare providers to deliver comprehensive and coordinated care. One way of doing this is by using a secure, encrypted internal staff digital communication system.
- Provide leadership development opportunities: Identify and nurture potential nurse leaders within your facility. Offer leadership development programs, workshops, and mentoring relationships to help junior and mid-level nurses develop their leadership skills.
- Recognize and reward excellence: Implement recognition programs to acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of nurses who excel in their roles. Celebrate achievements, whether it’s delivering exceptional patient care, implementing innovative practices, or contributing to quality improvement initiatives.
- Continuously evaluate and improve: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your nursing hierarchy and identify areas for improvement. Seek feedback from nurses, patients, and other stakeholders to gain insights into your staff work culture and system.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare facilities can optimize their nursing hierarchy, promote a positive workplace culture, and ultimately enhance patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Conclusion
The nursing hierarchy has immediate and far-reaching effects on patients, staff, and the way a facility runs. While there are aspects of the nursing hierarchy that can weigh down staff interactions, these can be improved by having a firm but empathetic leadership structure, willingness to adopt ways to optimize the nursing hierarchy, and guidance for staff on how to leverage the best potential from the way the health facility is set up. The advantages of the nursing hierarchy are powerful and numerous. Being open to these benefits can bring improved collaboration among healthcare staff, and your health facility can look forward to delivering better care with better patient outcomes.
FAQs about the nursing hierarchy
What is the chain of command in nursing?
The chain of command is useful when a technical or clinical patient-related issue needs to be resolved. The levels of nursing authority begin at entry-level and progress to the advanced level until senior-level nurses. The issue ‘travels’ upwards through the nursing levels in the nursing hierarchy until it is resolved. A typical chain of command is:
1. nurse assistants
2. staff nurse
3. charge nurse
4. nurse supervisors
5. team managers
6. nurse managers
7. department managers
8. hospital supervisors
9. the chief nursing officer







