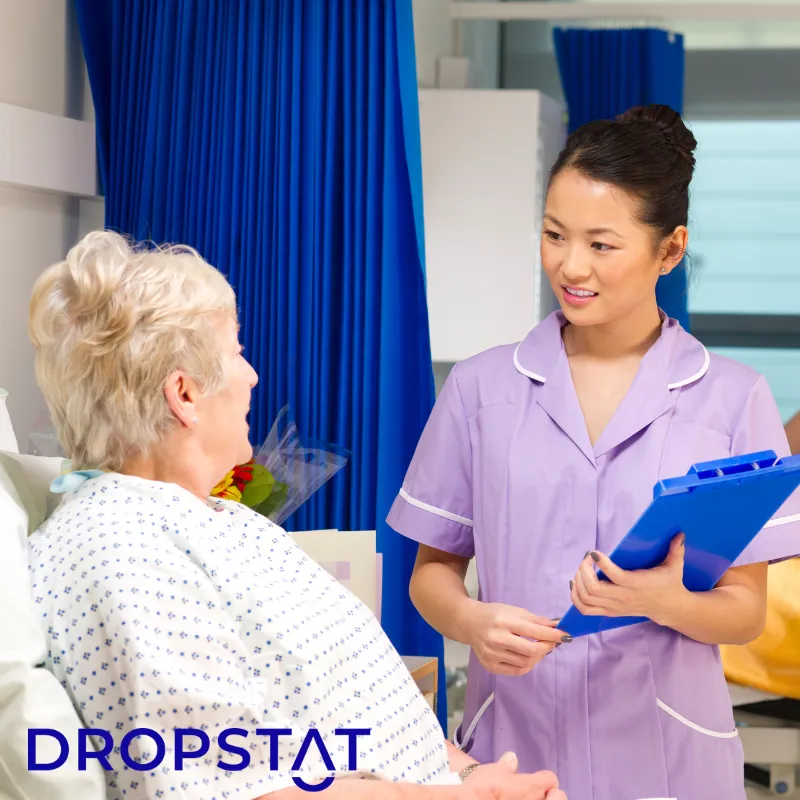
Research shows that where there is a good patient-nurse relationship, hospital stays are shorter. Nurses who combine good communication and clinical strategies are priceless caregivers.
What is effective communication in nursing?
Effective communication in nursing involves exchanging ideas, instructions, thoughts, opinions, and knowledge in a healthcare setting. Through effective communication, information is received and understood by patients and healthcare staff with clarity and purpose.
Effective communication helps nurses to achieve their goals in the best way possible for patient care tasks or tasks carried out with other healthcare professionals.
Who is involved in nursing communication?
Here are the 3 main dynamics in the healthcare system and several common scenarios.
1. Communication between nurses and superiors or senior healthcare professionals
- Nurses give verbal and written communication about patient health.
- They ask superiors or senior healthcare personnel for guidance and advice.
- They need to share technical information or implement a method in the nursing process.
- Nurses are responsible for advocating for patients.
2. Nurse-patient communication
- Nurses educate patients about treatment plans and answer their questions.
- They identify with patient worries and provide support.
- Nurses communicate with patients while caring for them (about 90% of patient care involves patients interacting with nurses.)
3. Communication among nurses
- Nurses communicate with each other in joint tasks and when helping each other with their tasks.
- They write or message other nurses for patient care and patient transfer.
- Nurses provide emotional support verbally or via internal chat systems to boost employee morale.

The importance of good communication skills in nursing
Effective communication between nurses and patients improves the quality of patient care and outcomes. When patients receive their treatment plans from nurses in a caring and clear way, they can follow them more accurately. Likewise, when patients feel understood and supported, they believe their care providers will effectively communicate their health plans and patient satisfaction increases.
When nurses can effectively communicate with each other, there is a greater sense of trust which promotes a positive work culture and improves nurse satisfaction.
Effective communication among staff and managers enables the facility to run smoothly and efficiently. When shift gaps are effectively communicated, nurses will be open to filling shift gaps, ensuring seamless shift schedules. Additionally, when nurses have a clear understanding of their job scope, this enhances engagement and productivity levels.
7 effective communication skills in nursing
Here are 7 essential communication skills your nurses need to make your facility stand out as the best.
- Clarity and brevity
Effective communication in nursing demands that nurses speak slowly and enunciate their words clearly. A short message is easier for a patient – who might be bewildered – to grasp.
Better patient outcomes depend on nurses’ clinical expertise in giving clear directions to each other, to patients, or to their family members. Instructions that could be easily misheard or misunderstood, like, “Take your medicine at nine,” which may sound like “Take your medicine at night,” should be stated in a non-ambiguous way, “Take your medicine after breakfast.”
This communication skill includes spoken and written communication.
2. Overcome communication barriers in nursing
Nurses must consider the many physical barriers to communication that patients might face. Five physical barriers to communication are:
- environment (e.g., a noisy, distracting area),
- distance (e.g., applicable especially to travel nurses or telenurses),
- time (e.g., patient care is delayed or the patient cannot come at the right time),
- medium (e.g., the patient cannot hear aural instructions or is illiterate with poor written communication skills) or
- technical difficulties (e.g., the patient has lost their glasses or phone).
Mental incapacity is another barrier to patient communication, such as for stroke survivors. Nurses must learn to give very simple short commands (“Big mouth, now swallow.”) for health promotion.
All these barriers can be overcome with planning and care. Nurses who can look at things from the patient’s perspective will display better patient understanding. They will change their communication style to match the health and mental ability of whomever they are talking to.

3. Non-verbal communication in nursing – Body language and facial expressions
Body language is one of the more subtle yet very powerful communication strategies in nursing. Body language can augment a nurse’s spoken instruction or request. If a shift manager is working on unifying the nursing team, using the hands in a general embracing gesture would give a message of unity. Body language can convey a nurse’s authority or compassion, submission, or respect.
Facial expression is one of the top nonverbal communication skills needed for communicating effectively. Facial expression can be helpful when educating patients. A smile, a thumbs up, and maintaining eye contact can show approval or understanding. Facial expression is such a good indicator of how people are feeling that it has been ‘borrowed’ for emojis and is commonly used for nurse satisfaction surveys and for collecting patient satisfaction scores.
Another use of the facial expression as a tool in healthcare is when young children or adults with limited communication ability are given a facial-emotion board. The nurse asks them to point to a face that shows how they feel.
Practically, nurses should ensure that their hair or headwear does not cover their mouth or eyes. Also, that body language is clear and not obscured (e.g., by flowy jackets) for other healthcare professionals or patients.
4. Treat others with respect
Cultural awareness helps nurses respect people of every culture. Successful nurse-patient communication is predicated on an attitude of mutual respect. The nurse-patient relationship will thrive in such an environment. Likewise, when nurses respect each other, patients will sense a genuine and meaningful relationship and will respect the nurses too.
Nurses can improve patient satisfaction scores by showing respect in communication. Here are some simple humanistic practices which help make personal connections.
- Knocking before entering a patient’s room or standing outside the curtained area and asking if it’s okay to enter.
- Introducing oneself. A patient enjoys knowing who is addressing them. Studies show that patients often do not recognize the name of their caregivers. A 2002 study found that patients could not recognize the name of their caregiver from a list of names 59% of the time.

5. Active listening.
Active listening means not just hearing the words someone says but seeking to understand the causes or intentions behind them. Understanding patient-provider conversations is an example of active listening, a sign of high-quality patient care. Patient-provider communication means the sharing of complete and accurate information about the patient’s care and adherence to treatment plans.
The success of strong nurse-patient communication with individual patients depends on specific patient preferences. But studies show that spending time sitting by the side of patients improved patient satisfaction scores and had a positive impact on patient outcomes. 91% of patients who felt frustrated due to a lack of communication wanted nurses to spend more time with them. These studies underline the importance of communication for nurses.
6. Being trusted and trusting others
Patient trust in nurses means that patients can rely on nurses for their healthcare needs with confidence. Nurse trust in patients means nurses can rely on patients to complete their healthcare plan as instructed. Trust significantly affects patient satisfaction scores, so facilities that achieve trust in both directions generally have stellar reputations.
On the nurse management side of things, nurses want to work in facilities that incorporate effective communication in nursing management. That can only happen when there is trust.
7. Assertive communication in nursing
Nurse leaders must use assertive communication in nursing when communicating with subordinate staff. This hierarchy ensures instructions from other health professionals will be followed precisely for better patient care. Assertive yet respectful communication for nurses encourages productivity but rejects nurse bullying.
When patients or their families communicate with nurses, there will also be some assertive communication. As long as it is respectful, it can be helpful. Understanding patient worries will encourage patient interaction and foster a better nurse-patient relationship. Patients’ families sometimes request the help of a nurse to advocate for a patient.
Patient education is one place where assertive communication is essential. Patient education means that patients are involved in their own care. Nurses must be assertive in this nurse-patient relationship for patient safety and to achieve the best outcomes.
FAQs
What is the most important nurse-patient communication skill?
The most important nurse communication skill is active listening while paying attention to verbal and nonverbal clues. A responsible nurse notices the patient’s facial expression and tone of voice. When a patient shares their experience and concerns, it is valuable information that can influence the outcome of the treatment.
Active listening applies in nurse-to-nurse communication too. Nurses can work in greater harmony and successfully navigate every interpersonal issue with active listening. The more nurses build an environment based on trust and respect, the more effective their communication will be.
What is the purpose of healthcare staff asking each other obvious questions about patients?
A 1997 study looked at the causes of miscommunication and difficulties in managing projects in healthcare. One major discovery was that people working in different disciplines understood words to mean different things. For example, “Patient readiness” to nurses meant that their patient was dressed but still in bed. However, to physical therapists, it meant that the patient was dressed, fed, and sitting in a wheelchair, ready to be transported to the floor where physical therapy took place.
Obviously, communication will be challenged when each discipline has its own definition of terminology. The study suggested that a nurse manager (project leader) should assume that healthcare staff from different disciplines do not understand each other. Therefore giving and receiving information is crucial. Also, asking apparently obvious questions and giving clear answers will help communication between disciplines. (Sapienza, A. M. (1997)
How Dropstat can improve communication in nursing
Dropstat can improve manager-nurse communication about available shifts by instantly communicating unfilled shifts to qualified staff and accepting nurses based on safety and seniority metrics. This streamlines the time it takes to fill shift gaps in your facility and means less expenditure on agency nurses and overqualified staff.
In addition, Dropstat includes a shift feedback feature, where nurses can rate their mood with an emoji after every shift. This facilitates communication of nurses’ overall satisfaction to the manager. This self-report updates managers continuously on the state of the facility’s work culture.
The unique combination of Dropstat’s features means that your nursing workforce can be managed more efficiently and cost-effectively. Schedule a demo to discover how your facility can benefit from seamless shift planning, improved work culture, and nurse satisfaction.