What does safe staffing mean?
Safe nurse staffing means an appropriate number of nurses available to care for patients, with the right education, skills, and experience to ensure that patient care needs are met. Furthermore, the working conditions and environment must also support staff to provide optimum care.
What is a safe staffing ratio in nursing?
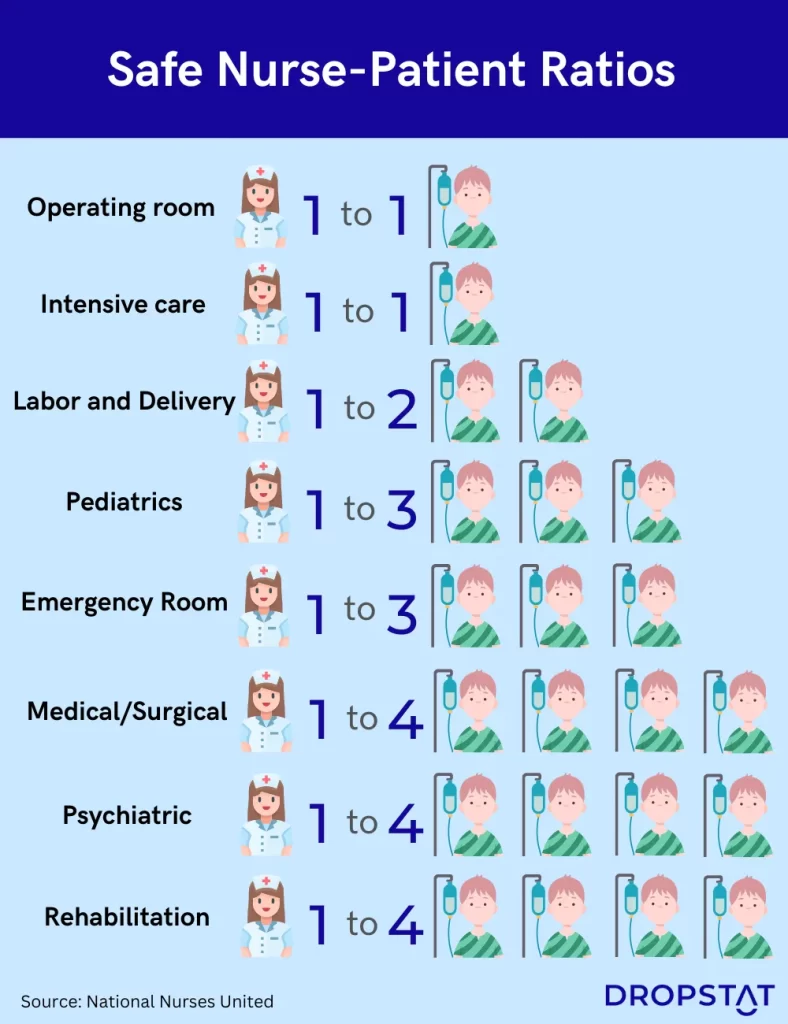
Although exact nursing safe staffing ratios are often disputed, below are some of the nurse-to-patient ratios that the National Nurses United recommends for safe staffing:
- Operating Room: 1:1
- Medical/Surgical: 1:4
- Emergency Room: 1:3
- Intensive Care: 1:1
- Psychiatric: 1:4
- Rehabilitation: 1:4
- Labor and Delivery: 1:2
- Pediatrics: 1:3
Use this tool to calculate safe staffing levels for your facility.
How does a lack of safe staffing in nursing affect patient care?
Unsafe staffing has proved to be a threat to the health and safety of patients in countless ways. The Journal of the American Medical Association notes that each additional patient nurses were required to care for was linked to a 7% increase in death within the first 5 days of admission. Alarmingly, higher numbers of patients per nurse were also strongly associated with administering the wrong medication or dose, pressure ulcers, and patient falls with injury.
An article from the Los Angeles Times reported that on June 23, 2022, nurses at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center participated in a one-day strike to raise awareness of the issues of being overworked, understaffed, and lacking in critical medical supplies. According to the article, Tinny Abogado, an RN of 20 years, explains that patient care is put at risk stating that 50 nurses have resigned, citing “poor working conditions.” The article also affirms that the staff is not equipped with adequate supplies such as syringes and IV kits, which makes it increasingly more difficult to care for patients properly.

An additional observational study conducted by the National Institute for Health and Care Research evaluated how staffing levels impacted patient care in a southern England hospital between 2012 and 2015. They found that increased patient mortality was linked to increased temporary staffing instead of permanent staff.
Through a review of over 40 studies, patient reports, and self-reports from nurses, the Patient Safety Network found that between 55% – 98% of nurses had failed to complete one or more required care tasks.
How to achieve safe nurse staffing in your facility
The first and most crucial step to ensuring safe nurse staffing is hiring enough staff to meet the recommended nurse-to-patient ratios at every shift. You’ll need to consider sick and vacation days for each staff member as well as fluctuating patient care demand during busier and quieter times in your facility. An adequate number of staff members working is the essential foundation for safe nurse staffing; however, other factors also contribute greatly to safe staffing and the quality of patient care.
- Adequate resources and supplies – there has to be enough of the right medication and equipment for nurses to provide proper patient care. It’s impossible to create a safe staffing environment when there are shortages of essential equipment that nurses need to assist patients.
- Teamwork – When nurses collaborate effectively, healthcare teams can improve patient outcomes, prevent errors, and increase patient satisfaction.
- Work environment and culture – A positive workplace culture can help reduce mortality rates, falls, injuries, and hospital-acquired infections.

How HPPD in nursing improves safe staffing
HPPD (hours of care per patient per day) is a metric that healthcare facilities use to calculate how many nurses to place in every unit so that each unit is fully staffed to meet regulatory levels. The HPPD metric can predict nursing care that will be missed if the safe staffing ratio is not kept at or above the legal minimum. National staffing minimums aim to guarantee the quality of care and allow nurses to spend more time with patients.
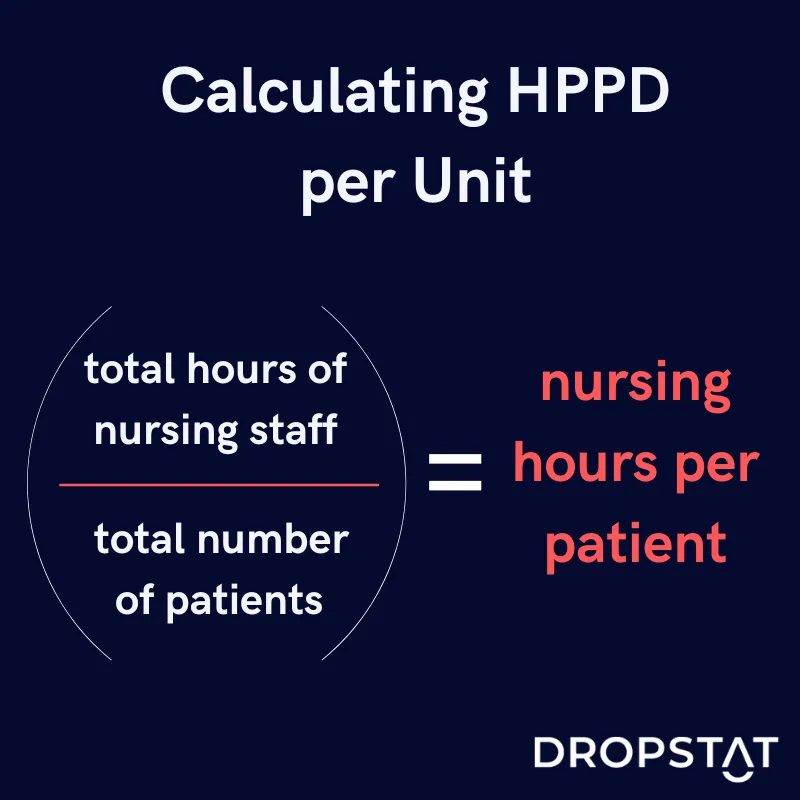
How to calculate hours per patient day
Making an hours-per-patient-day calculation yields the number of hours nurses deal directly with patients and manage indirect care. A unit with greater patient acuity will have a higher HPPD than a unit with lower acuity. One way of calculating HPPD is by taking the number of the total productive hours of the nursing staff (RN, LPN, CNA, GNA) per unit and dividing it by the total number of patients per unit.
The optimal HPPD figure depends on the needs of each type of patient. Legal minimum requirements vary with state, standing between 3 to 3.6 direct care hours per patient per day. Some states differentiate between the amount of direct care given by a nurse or a nursing assistant.
How do facilities gain from having safe staffing ratios?
Apart from increasing the quality of patient care as well as reducing morbidity rates, adequate staffing also directly lowers:
- Nurse turnover rates – Safe staffing ratios help nurses feel less overworked and create higher patient satisfaction, contributing to nursing retention.
- Nurse burnout – Nurses feel overloaded, strained, and emotionally exhausted when they are not working with a big enough team of staff to provide optimum patient care. Having safe nurse staffing ratios is very effective in preventing staff burnout.
- Excess Spending – Increased nurse staffing is a more cost-effective way to improve patient care than having fewer staff on board.
“After ratios were implemented in California, hospital income rose dramatically from $12.5 billion to more than $20.6 billion” (source: nysna.org)
If nurses have a larger team, they can distribute the mental, emotional, and physical demands of their daily tasks by allowing for appropriate breaks and the ability to seek out support from additional staff. By doing so, patients interact with a team of nurses who can evenly distribute critical care tasks and subsequently deliver significantly better patient care.
How Dropstat helps facilities keep safe nurse-patient ratios
Safe staffing ratios can be easily incorporated into the healthcare system with Dropstat’s automated scheduling platform. With Dropstat, healthcare facilities can ensure adequate nurse-to-patient ratios without relying on temporary staffing and other expensive options. Dropstat enables schedulers to keep track of overtime while posting open shifts well in advance in anticipation of short-staffing. The cost-effective methods that Dropstat uses to fill shift gaps save the facility money on staffing that it can use for critical supplies and other resources.
Frequently asked questions
What are the reasons for unsafe staffing in nursing?
Below are some typical reasons for understaffing in nursing:
– The facility has a high nurse turnover rate due to a lack of administrative support and unhealthy work environments.
– The facility is reluctant to hire more staff.
– There is a shortage of nurses with the right level of skills looking for jobs.
What is the minimum nurse-to-patient ratio?
The recommended staffing ratio in teaching hospitals is to have 1:3, and in general hospitals, 1:5, including a senior nurse.
Is there a link between nurse staffing ratios and patient outcomes?
Research has proven a link between safe nurse staffing ratios and patient outcomes. Numerous studies have found that when nurse staffing ratios are lower, patient outcomes are worse, including higher rates of complications, infections, medication errors, and mortality.
On the other hand, increasing nurse staffing levels can improve patient outcomes. A study published in Health Services Research found that increasing nurse staffing levels were associated with decreased patient mortality and hospital length of stay.
Conclusion
By ensuring a safe staffing ratio in your facility, you will keep costs to a minimum, protect your nurses’ health, and provide the best care for your patients. Not sure where to start? Schedule a demo now to take advantage of Dropstat’s scheduling features and make safe staffing a priority in your facility. Dropstat’s app removes the burden of filling shifts and guarantees the optimal staff-to-patient ratios in your facility.






