What is a medication error in nursing?
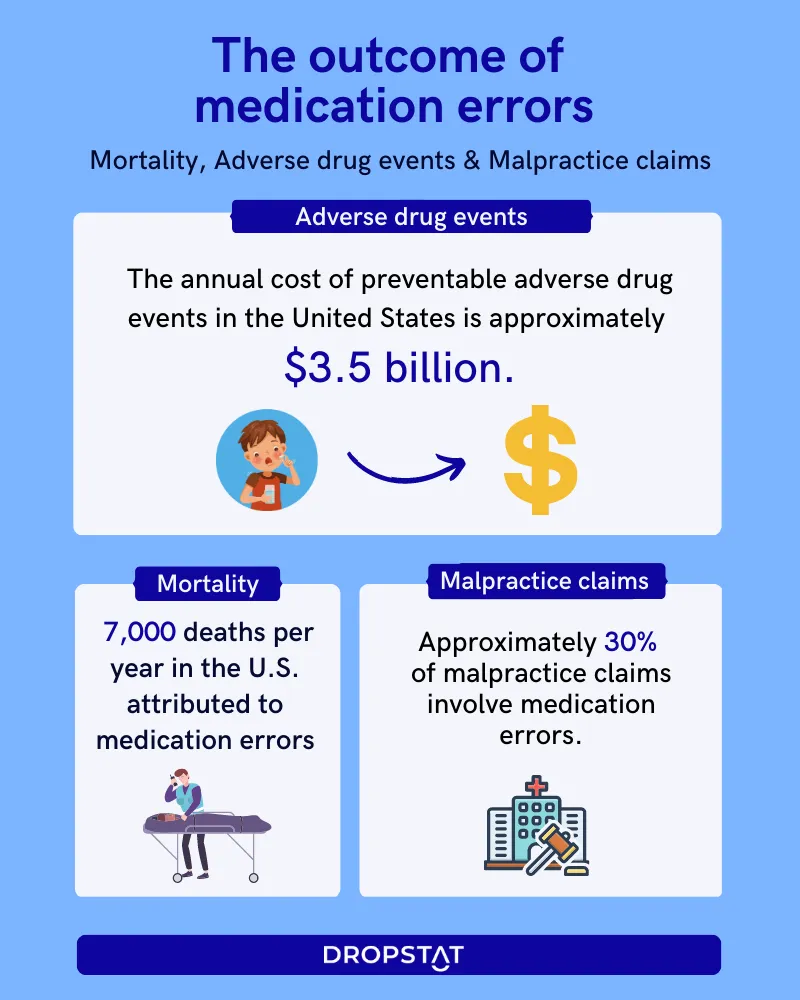
Medication errors refer to avoidable, incorrect use of medication or harm rendered to a patient while prescribing, preparing, dispensing, or administering medication. Medication errors can occur in any healthcare setting, including hospitals, nursing homes, and outpatient facilities. Medical errors in healthcare are a major problem in healthcare facilities worldwide, causing an estimated 7,000 deaths per year in the U.S. alone.
The importance of preventing medication errors in nursing
Medical errors in nursing are a significant concern for healthcare facility CEOs, as they can result in serious harm to patients. Statistics on medication errors in nursing are alarming. The NCSBN (National Council of State Boards of Nursing) states that medication errors are the most common type of medical error in nursing. In a study on medication errors in hospitals, it was found that medication errors occurred in 19.1% of medication administrations.
No healthcare facility wants to be the target of negative attention. Patients want to be safe and healthy and do not want to suffer from the effects of medication errors. For these reasons, healthcare managers must focus on preventing medical errors as much as possible by being aware of potential pitfalls and committing to the best preventative practices in administering medications.

What are the consequences of medication errors in nursing?
Medication errors in nursing can have serious consequences for patients. Depending on the type and severity of the error, the results can range from mildly annoying symptoms to being fatal and life-threatening. Some consequences of medication errors in nursing include:
- Adverse drug reactions: Medication errors can cause adverse drug reactions, which are unexpected, harmful reactions to a medication.
- Increased hospital length of stay: Medication errors can lead to increased hospital stays, as patients may require additional treatment to address the consequences of the error.
- Increased mortality rates: In severe cases, medication errors can result in patient deaths. NASEM says that medication errors cause an estimated 1.5 million adverse drug events in the United States each year, resulting in approximately 7,000 deaths.
- Poor public facility image: Medication errors can damage the reputation of healthcare facilities, as patients and their families become wary of seeking care at facilities that have a reputation for medication errors.
- Lawsuits: Medication errors can lead to lawsuits against healthcare facilities and healthcare professionals, which are costly and time-consuming.
- Financial costs: Medication errors can also result in financial costs, such as the cost of additional treatment, lost workdays, and compensation for patients who have experienced harm due to the error.
Overall, medication errors in nursing can have serious consequences for patients, healthcare facilities, and healthcare professionals. Preventing medication errors should be a top priority for all healthcare organizations to ensure the safety and well-being of patients.
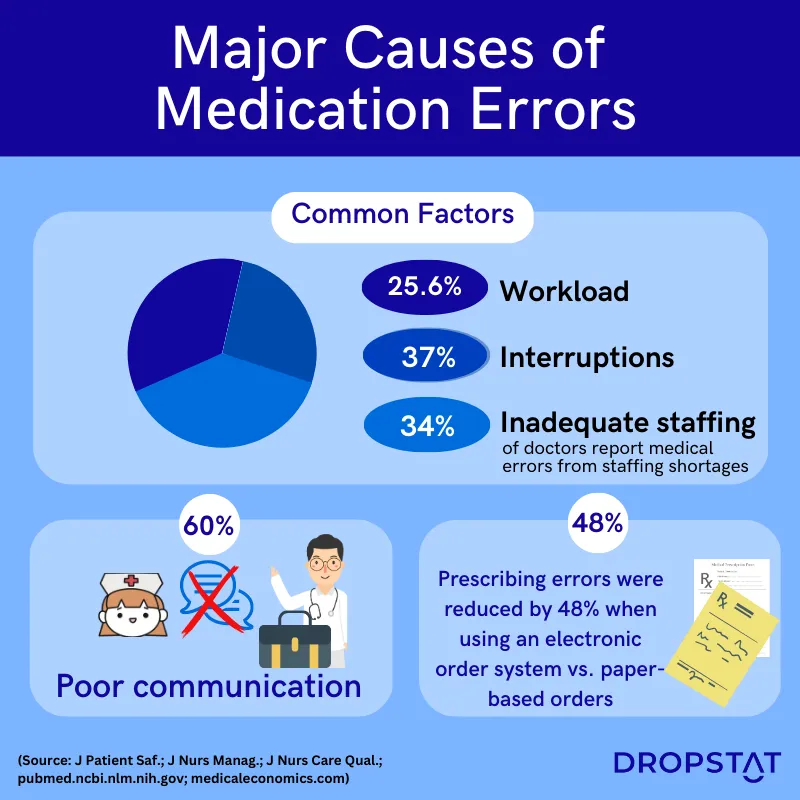
Common causes of medication errors in nursing
Several factors contribute to medication errors in nursing. Here are some common causes:
- Lack of communication
Communication breakdown between healthcare professionals can result in medication errors. For instance, a doctor may prescribe a medication without considering a patient’s allergies or other medications they are taking. Without proper communication, nurses may administer such medication, causing adverse reactions. At nursing handoff, nurses must make sure to share important patient information, even if it is written somewhere in the patient’s notes.
- Lack of proper training
Nurses may not receive adequate training in medication administration. This can lead to mistakes such as administering medication via the wrong route or at the wrong dose.
- Heavy workload
Nurses often have a heavy workload, which can result in fatigue and stress, and reduced awareness. This can lead to errors such as administering medication to the wrong patient or forgetting to administer medication at the correct time. More nurses must be brought in from internal resources, float pool nurses, or from an agency to prevent nurse overload.
- Poor medication labeling
Poor labeling of medication can lead to errors, such as administering the wrong medication or dose. Medication labeling should be clear and easy to read.
- Distractions and interruptions
Nurses who are interrupted while administering medication may become distracted and make errors, such as administering medication to the wrong patient or giving the wrong dosage.
- Inadequate patient information
Nurses who do not have access to complete and accurate patient information, such as medication history, allergies, and medical conditions, may make medication errors.
Examples of medication errors in nursing
Some medication errors that occur in hospitals take place with commonly administered drugs. Common types of medication errors in nursing include:
- Administration of the wrong medication: This occurs when a nurse gives a patient a medication that is not prescribed for them.
- Administration of the wrong dosage: This happens when a nurse gives a patient too much or too little of the medication.
- Failure to administer medication: This transpires when a nurse forgets to give a patient their medication at the prescribed time.
- Administration of medication via the wrong route: This takes place when a nurse gives medication to a patient via the wrong route, such as giving an oral medication intravenously.
- Medication reconciliation errors: This follows after a nurse fails to accurately document a patient’s medications or fails to update the patient’s medication list when changes are made.
- Transcription errors: This ensues when a nurse writes down the wrong medication or dosage when transcribing the prescription.
- Medication dispensing errors: This problem arises when a nurse dispenses the wrong medication or dosage to a patient.
- Allergic reactions: This issue presents itself when a patient has an allergic reaction to a medication that was not properly identified in their medical history.
- Drug interactions: This problem turns up when a patient is given medications that interact with each other and cause unwanted, harmful effects.
There are many more types of medical errors. It is important for healthcare facilities to have protocols in place to prevent errors and ensure the safety of patients.
Prevention of medication errors in hospitals
Hospitals and outpatient clinics are often big facilities with a great concentration of patients in them. Each patient has an individual health plan with different needs. Preventing medication errors in nursing often requires applying several preventative strategies at once:
- Enhance communication: Healthcare professionals must communicate effectively to prevent medication errors. This can be achieved through clear documentation of medication orders, effective handovers between shifts, and regular team meetings.
- Proper training: Nurses must receive adequate training in medication administration to prevent errors. Training should cover topics such as medication routes, dosage calculations, and medication interactions.
- Reduce workload: The general workload of nurses should be reduced to minimize fatigue and stress. This can be achieved by hiring more nurses or implementing technological solutions that make procedures easier for nurses.
- Clear labels on medication: Medication labeling should be clear and easy to read. Labels should include the patient’s name, medication name, strength, dosage, and route of administration.
- Involve patients: Involve patients in their own healthcare and inform them about their medications and treatment. This can help to prevent errors such as medication interactions and allergic reactions.
- New solutions: New solutions in the prescription and administration of medication, such as doctors sending electronic prescriptions directly to the pharmacy, saving portable electronic medication records, and using automated medication dispensing systems, can help to prevent medical errors.

Prevention of medication errors in nursing homes
Medication errors in nursing homes are of particular concern since the patients are elderly and they may have complex medication regimes. Often elderly patients are not involved in their medication, so they cannot be relied upon as a backup for confirming the correct medication or dose. Some strategies to prevent medication errors in nursing homes are:
- Double-check: Nurses should double-check (two nurses) medication directives before administering drugs to patients to reveal any potential medication errors.
- Use automation in dispensing medication: Use advanced electronic systems to record prescriptions, dispense and administer medications, with age and health issues of the patient in the system, and an alert would sound whenever there is a potential problem.
- Verify patient identification: Nurses should verify a patient’s identity before administering medication every time to ensure that the correct medication is given to the correct patient.
- Train staff sufficiently: Nursing home staff must receive adequate training in medication administration for older patients, including medication routes, dosage calculations, and medication interactions.
- Review medication regularly: Medication schedules should be reviewed regularly by nurses and doctors to ensure patient safety.
- Inform: Inform the patient and their family members of the drugs they are receiving and make an electronic note after the drug is administered, including the numbers, e.g., batch date.
- No exhaustion in nurses: Make sure nurses are fresh and rested at the beginning of the shift. Almost 5% of all medical errors happen with nurses that are working mandatory overtime hours (Michigan Nurses Association and other studies).
How Dropstat helps prevent medication errors in nursing
Dropstat, an AI-powered scheduling app, helps healthcare facility managers stay 100% vigilant of staff who are entering overtime status. Apart from sidestepping the avoidable expense of overtime, schedulers help patients stay safe since nurses who work overtime are at a much greater risk of making medication errors. The system keeps track of nurses who are working overtime and alerts schedulers if a nurse will be going into overtime by picking a shift. The scheduler can decline these nurses from taking on additional shifts and save patients from the great risks of exhausted nurses.
Schedule a demo today to take a step towards keeping your patients safer by avoiding medication errors in nursing.







