Prioritizing interoperability in healthcare allows healthcare information technology (HIT) to be exchanged and utilized more efficiently for the purpose of making data-informed decisions. The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH), part of the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA), promotes the use of electronic health records and expands the privacy and security regulations under HIPAA. Widening the utilization of digital records across healthcare settings improves patient experience while integrating care teams for a more holistic approach to healthcare delivery.
Why is interoperability important in healthcare?
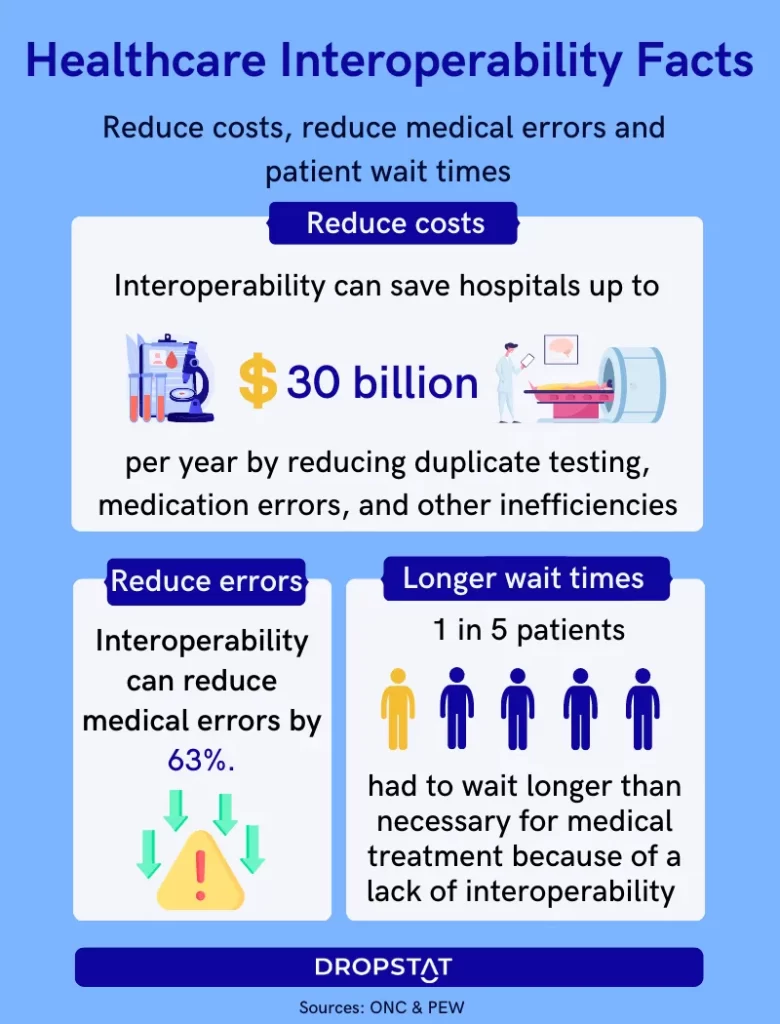
Health data interoperability reduces the need for replicated services such as tests and imaging, which in turn decreases healthcare spending for both patients and facilities. Specifically, when health systems provide proper access to clinical data, hospital readmissions, unnecessary treatments, and many common medical errors are avoided as a result of increased care coordination and communication.
Types of Healthcare Interoperability
There are four common types of interoperability within the healthcare sector, which are classified by different data-sharing methods. These different categories include:
Foundational interoperability
This level of interoperability aims to connect different health information systems to one another but does not ensure that the receiving system can interpret the data. For example, this level of data enables one healthcare facility to send test results to another, although the facility that receives the data can only analyze the results if it has the necessary software.
Structural interoperability
When two or more systems exchange and interpret data through a standardized format, more IT systems and providers can utilize patient information. Health Level 7 (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) are two data exchange standards that promote this level of interoperability.
Semantic interoperability
While structural interoperability allows for data to be exchanged and interpreted through standardized methods, semantic interoperability ensures that the data can be understood and used by any receiving system. It also simplifies the sharing of patient data among numerous providers.
Organizational interoperability
Lastly, organizational interoperability refers to the process of generating business processes to securely and accurately transfer and use data. This level of interoperability is effective both internally and among different establishments. Organizational interoperability requires instituting policies and procedures that maintain effective data-sharing methods. Furthermore, utilizing this form of interoperability promotes greater coordination between various parts of the healthcare system (such as public health agencies and hospitals) to collaborate for the shared goal of enhancing patient outcomes.
When interoperability in healthcare is implemented effectively, healthcare providers can deliver higher quality care while reducing healthcare costs, engaging in value-based care, and meeting regulatory compliance requirements. Implementing and assessing all four levels of interoperability is crucial to achieving functional interoperable systems.

The benefits of interoperability in healthcare
Many healthcare challenges can be mitigated by integrating interoperable systems within your current practices. The main benefits of interoperability in healthcare include the following:
- Improved patient care
Providers can make better data-informed decisions when healthcare organizations take advantage of interoperability through electronic health records and other health software. In addition, simplifying data-sharing promotes greater care coordination between different members of a patient’s care team, which contributes to better patient outcomes and more effective treatment and discharge plans.
- Reduced healthcare costs
One main advantage of interoperability in healthcare, specifically, is the reduction of repetitive tests and imaging. Enabling access to patient data also helps providers avoid duplicate services and potential medical errors, thereby reducing readmissions and the cost of care.
- Increased operational efficiency
Interoperability assists healthcare facilities in reducing the administrative burden with the goal of streamlining common tasks such as accessing patient records and immunization charts. This increase in automation promotes a greater focus on patient care as opposed to spending time on billing or scheduling. Focusing on patients more contributes to higher patient satisfaction ratings.
- Helps reduce burnout among providers
When providers can rely on healthcare software and interoperability to complete repetitive tasks, easily retrieve patient health information, and access decision-making support, facilities experience less nurse burnout. The decrease in time spent on easily automated tasks boosts employee job satisfaction and enhances employee engagement.

Barriers to implementing interoperability within a healthcare organizations
Although interoperability improves healthcare quality and patient outcomes, there are some barriers to implementing these practices as well. Some of the main challenges include concerns about patient privacy and data security, ensuring standardized data formatting, and hesitancy from providers.
CMS efforts to promote interoperability standards in healthcare
The CMS Newsroom provides information to the public about CMS’s Interoperability and Patient Access Final Rule establishes methods to give patients more access to their own health data. In doing so, patients can become more informed about their own care and prominent members of their healthcare team, which lays the foundation for better patient-provider communication and patient engagement.
Health Information Exchange (HIE) and Data Sharing Methods
Health Information Exchange (HIE) is a network of health data that different providers and organizations can access and must meet national data-sharing standards. The HIE is a major aspect of interoperability in healthcare that allows providers to retrieve and safely share patient health information. HIE works alongside electronic health records in a standardized format, making critical patient data easier to share and use. When providers and patients opt into the HIE, clinicians can make more patient-specific treatment plans and reduce the cost and overuse of healthcare services which reduces healthcare costs overall.
Prioritizing interoperability within your healthcare institution prepares your staff to deliver optimal care while reducing costs and burnout.







