What is remote patient monitoring?
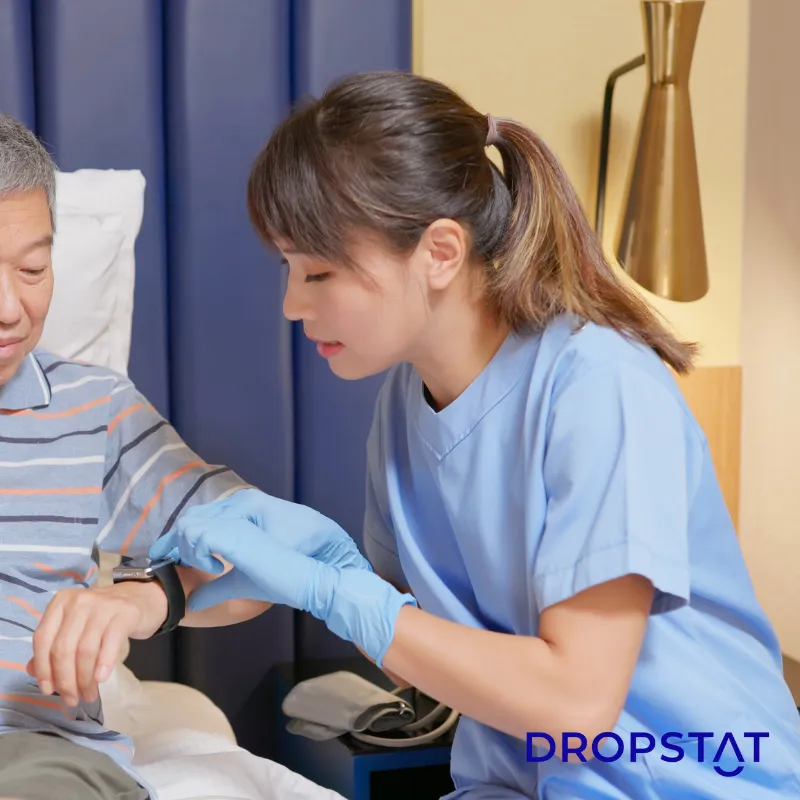
The definition of remote patient monitoring (RPM) refers to a healthcare approach that utilizes advanced technology to collect and monitor patient health data remotely. Patients use or wear specialized wearable devices or sensors that track vital signs, activity levels, and other health parameters. This data is securely transmitted to healthcare personnel, who provide real-time insights into the patient’s well-being and proactively intervene as necessary. Remote patient monitoring is more about collecting medical data, yet it is a subset of telehealth.
How does remote patient monitoring work?
Remote patient monitoring is facilitated by specialized software designed to collect, transmit, and analyze patient health data. This data is acquired through a range of remote patient monitoring devices, including wearable technologies, sensors, and monitoring tools. This is how RPM works
1. Data collection: Patients use remote patient monitoring devices to track vital signs, symptoms, and other relevant health parameters. These devices continuously gather data, ensuring a comprehensive view of the patient’s health status.
2. Data transmission: The collected data is securely transmitted to the remote patient monitoring system in real-time, enabling healthcare providers to access and review it promptly. This instantaneous data transfer allows for punctual interventions and informed decision-making.
3. Data analysis: Remote patient monitoring software employs advanced algorithms to analyze incoming data. It detects patterns, trends, and deviations from baseline statistics, providing valuable insights into the patient’s health condition.
4. Care management: Healthcare providers observe the data analyses, create personalized care plans for patients, make proactive interventions, and remotely monitor the patient’s progress. RPM enables early detection of potential health issues and gives patients more time to adjust to treatment plans.
What is wearable technology in healthcare, and how is it related to remote patient monitoring?
Wearable technology in healthcare refers to the innovative devices used for remote patient monitoring. These devices include smartwatches, fitness trackers, biosensors, and other specialized medical wearables in various formats, such as watches, rings, straps, patches, headbands, and finger clips.
Wearable technology harnesses the potential of evolving technology in the Internet of Things (IoT) to facilitate and promote remote patient monitoring solutions. By seamlessly integrating with patients’ daily lives, wearable technology enables continuous monitoring of consumers’ health parameters.

Examples of remote patient monitoring devices
The wearable device market is constantly evolving and expanding. There are many different wearable devices available in the market today.
Here are five examples of popular remote patient monitoring devices in healthcare, with a brief description of how each device works and how it improves health outcomes.
Smartwatches
Smartwatches, such as the well-known Apple Watch or Fitbit, have become widely used for remote patient monitoring. These devices typically have built-in sensors that track heart rate, activity levels, sleep patterns, and more. By wearing a smartwatch, patients can continuously monitor their health parameters and transmit the data to healthcare providers. The data collected helps identify irregularities, detect changes in health status, and enable timely interventions, leading to improved health outcomes.
Blood glucose monitors
For patients with diabetes, remote monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. Blood glucose monitors, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, allow patients to measure and track their blood sugar levels throughout the day. CGM systems provide real-time data and alerts, helping patients manage their diabetes more effectively. By facilitating proactive health management and enabling timely adjustments in medication and lifestyle choices, remote blood glucose monitoring improves health outcomes for diabetic patients.
Blood pressure monitors
Remote blood pressure monitors enable patients to measure and monitor their blood pressure at home. These devices, often in the form of an upper arm cuff or wristband, provide accurate readings and transmit the data to healthcare providers. By regularly monitoring high blood pressure, patients and their healthcare providers can identify trends and changes, allowing for early detection of hypertension or fluctuations. This enables healthcare providers to intervene promptly, adjust medications if necessary, and provide lifestyle recommendations, leading to better control of high blood pressure and improved cardiovascular health outcomes.
Pulse oximeters
Pulse oximeters are portable devices that measure oxygen saturation levels and heart rate. They are commonly used for monitoring respiratory conditions such as COPD, a pulmonary disease, or during the COVID-19 pandemic. Patients can easily clip the device onto their fingers and receive real-time readings of oxygen levels in the blood. Remote monitoring of pulse oximetry data enables healthcare providers to detect hypoxemia or changes in oxygen saturation levels, facilitating timely interventions and preventing respiratory complications.
ECG monitors
ECG (electrocardiogram) monitors, often in the form of wearable patches or handheld devices, record the electrical activity of the heart. These devices enable patients to capture and transmit ECG data to healthcare providers for analysis. Remote monitoring of ECG data allows for early detection of arrhythmias, irregularities, or changes in heart function. By promptly identifying cardiac issues, healthcare providers can intervene with appropriate treatments, medications, or referrals to specialists, thereby improving cardiac health outcomes.

What is the impact of remote patient monitoring and wearable technology on healthcare?
The impact of remote patient monitoring and wearable technology on healthcare is significant in managing diseases, especially chronic diseases, the cause of over 70% of deaths globally, and maintaining healthcare consumer well-being. These impacts include:
Enhanced patient care
Remote patient monitoring empowers healthcare providers to deliver proactive and personalized care. With a remote patient monitoring system in place, healthcare professionals can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs, activity levels, and other health data. Real-time data enables early detection of health issues. Remote monitoring ensures better health outcomes and improved patient care by proactively managing chronic conditions and identifying changes in patient health status.
Improved patient engagement
Healthcare provision is far more effective since wearable technology plays a vital role in engaging patients and promoting self-management. Wearable devices enable patients to monitor their health parameters conveniently, which guarantees patient safety . Patients more easily become active participants in their own health care, with a sense of responsibility and empowerment. By tracking their progress, adhering to treatment plans, and receiving real-time feedback, patients are motivated to make positive lifestyle changes and take charge of their well-being.
Enabling greater application of telehealth
The integration of remote patient monitoring with wearable devices increases the potential for telehealth services. It further enhances access to care and improves patient outcomes. Telehealth consultations combined with remote patient monitoring enable virtual visits, where healthcare providers can remotely review patients’ health data, conduct assessments, and provide timely guidance. This combination ensures continuity of care, particularly for patients with limited mobility, living in remote areas, or facing transportation challenges.
Improvements in wearable technology
The developments in healthcare and technology complement each other. As consumer desire for wearable devices and convenience grows, developers are only too happy to supply that demand.
Additionally, the rapid advancements in wearable technology have expanded the possibilities for remote patient monitoring, and the range of wearable devices continues to grow. These devices capture data beyond vital signs, including sleep patterns, activity levels, and even electrocardiograms. The continuous development of innovative sensors and devices enhances the accuracy and reliability of the collected data, facilitating more informed clinical decisions and personalized care plans.

The financial advantages of remote patient monitoring
Remote patient monitoring promotes effective cost containment in healthcare for patients and healthcare organizations. Overall, RPM facilitates optimizing the use of finite and infinite healthcare resources.
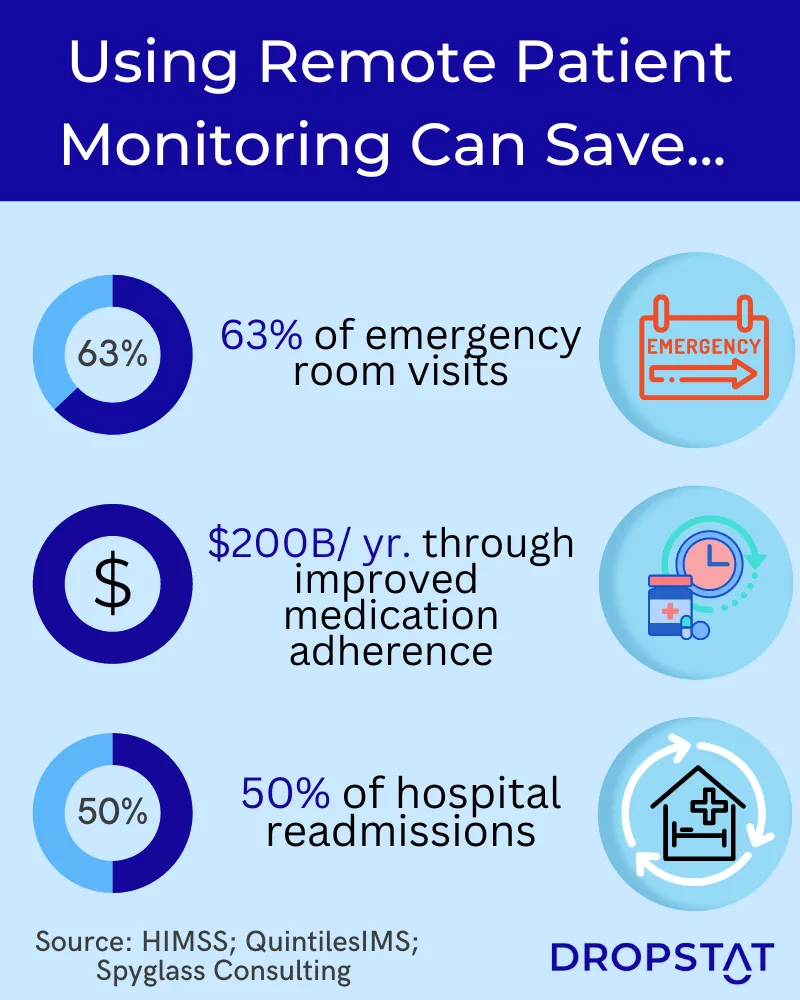
Patients notice savings in healthcare expenses as RPM helps patients save on healthcare costs by minimizing travel time and expenses for emergency room visits, hospital admissions, and outpatient appointments. Patients can avoid costly medical procedures by staying healthier as a result of preventative care, early intervention, and improving their medication and health plan adherence. Patients with chronic conditions or complex care can avoid frequent healthcare visits and have smoother daily routines allowing them to remain productive.
Additionally, many insurance providers now offer reimbursement for remote patient monitoring services and devices, including the cost of devices, monitoring services, and data transmission. This financial assistance reduces the out-of-pocket burden for patients seeking remote monitoring solutions.
Healthcare organizations notice savings in expenses primarily because the CMS (America’s Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) has recognized the value of remote patient monitoring and has implemented reimbursement policies to support its adoption. Reimbursement codes specific to remote patient monitoring services, such as CPT codes 99453, 99454, and 99457, provide financial incentives for healthcare facilities. These reimbursement opportunities encourage the implementation of remote patient monitoring systems and help healthcare organizations offset the costs of technology acquisition and maintenance, contributing to the financial sustainability of the healthcare organization.
This goes hand in hand with having digital health tools to
- Prevent acute exacerbations and the resultant hospital admissions and readmissions
- Reduce the strain on ED (emergency department) resources
- Allocate resources for patients more efficiently through automated patient prioritization
- Improve care coordination, communication, and operational efficiency, and reduce administrative costs
- Monitor chronic disease more efficiently
What are the challenges of remote patient monitoring?
Implementing and integrating these technologies into healthcare systems also pose certain challenges. It is essential to address these challenges in the healthcare system to ensure successful adoption and utilization.
Data system requirements
One challenge in remote patient monitoring is the need for robust data management systems with secure storage, efficient transmission, and effective analysis.
Interoperability
Another challenge lies in the complexity of interoperability in healthcare regarding wearable devices and existing healthcare systems. Integrating wearable technology with electronic health records (EHR) and other healthcare platforms collaborate requires seamless data exchange.
Patient education
Healthcare facility CEOs must implement patient education programs and emphasize the benefits of wearable technology while providing ongoing support to promote patient compliance.
Cost of infrastructure
Cost is another consideration when implementing remote patient monitoring and wearable technology. Healthcare facility CEOs must assess the financial implications of acquiring and maintaining the necessary devices and infrastructure.
Privacy and security
Lastly, regulatory and privacy considerations add complexity to adopting remote patient monitoring. Healthcare facility CEOs must navigate compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and ensure that patient data is handled in accordance with privacy laws.
The future of remote patient monitoring in the healthcare industry
As we look ahead, RPM shows a promising future and will continue to shape the healthcare landscape. Here are some of the key aspects highlighting the future of remote patient monitoring:
1. Advances in wearable technology
Wearable devices will become more sophisticated, compact, and user-friendly. Future wearable technology will offer enhanced capabilities for monitoring a wide range of health parameters, including blood glucose levels, respiratory rates, and even mental health indicators. These advancements will provide healthcare providers with more comprehensive and real-time data, enabling more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
2. Integration of artificial intelligence (AI)
AI will certainly have a pivotal role in the future of RPM. Machine learning algorithms will analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict potential health issues. This integration of AI will facilitate early interventions, improve clinical decision-making, and empower healthcare providers to deliver proactive and targeted care.
3. Virtual care and telehealth expansion
RPM will continue to drive the growth of virtual care and telehealth services. The future will witness a seamless integration of remote patient monitoring with telehealth platforms, allowing healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations, monitor patients remotely, and offer timely interventions. This integration will enhance access to care, particularly for patients in rural or high-risk patients in underserved areas, and reduce the patient recovery burden on traditional healthcare settings.
4. Improved patient engagement and empowerment
The future of RPM will prioritize patient engagement and empowerment. User-friendly interfaces, personalized health insights, and interactive platforms will encourage patients to actively participate in their own care. Patients will have greater control over things that matter to them: weight gain, caring for chronic conditions, the availability of medical devices, and access to their health data, leading to a more collaborative relationship with healthcare providers and improved adherence to treatment plans.
5. Population health management
RPM will play a vital role in population health management strategies. By remotely monitoring individuals with chronic diseases or specific health risks, healthcare organizations can identify population-level health trends, implement preventive measures, and allocate resources more effectively. This proactive approach will lead to better health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and improved population health overall.
6. Regulatory reforms and reimbursement expansion
Governments and healthcare regulators are recognizing the value of RPM and its potential to transform healthcare delivery. In the future, we can expect regulatory reforms that support the wider adoption of remote patient monitoring. Reimbursement policies will expand to include a broader range of RPM services, incentivizing healthcare providers to invest in these technologies and ensuring sustainable implementation.

Remote Patient Monitoring FAQs
What is remote patient monitoring vs. telehealth?
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) involves using technology to collect and transmit patient health data remotely, enabling healthcare providers to monitor and manage patients’ conditions outside of traditional healthcare settings. Telehealth is different in that it refers to the delivery of healthcare services and consultations through telecommunication technology, such as video calls or phone calls. While both RPM and telehealth utilize mobile technology in healthcare, RPM specifically focuses on continuous monitoring and data collection, while telehealth encompasses a broader range of healthcare services delivered remotely.
What are the CMS guidelines for remote patient monitoring?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has established guidelines for remote patient monitoring services. These guidelines outline the requirements for reimbursement, documentation, and coverage of remote patient monitoring under specific billing codes. CMS emphasizes the need for active monitoring, interpretation of data, and communication with patients or caregivers to qualify for reimbursement. Compliance with these guidelines ensures that healthcare providers can receive reimbursement for remote patient monitoring services provided to eligible patients.
What are remote patient monitoring CPT codes?
Current procedural terminology (CPT) codes are used to report and bill for medical services, including remote patient monitoring. CPT codes specific to remote patient monitoring cover various aspects, such as initial setup and patient education, device supply, and monitoring and interpretation of patient data. Examples of remote patient monitoring CPT codes include 99453 (remote monitoring setup), 99457 (remote monitoring treatment management services), and 99458 (additional remote monitoring treatment management services). These codes help healthcare providers accurately document and bill for remote patient monitoring services provided to patients.







