Many healthcare leaders struggle with insufficient cybersecurity systems and a lack of funding for protocols to protect their organizations from cyber attacks. The significant rise in attacks from 2021 to 2022 underscores the growing vulnerability of the healthcare sector to cyber threats. A great percentage of the largest cyber-attacks of 2022 targeted healthcare organizations. For example, 30% of large data breaches came from cyber attacks on hospitals. These facts indicate the urgent need for taking robust cybersecurity measures and proactive defense strategies – to protect patient information, maintain operational continuity, and safeguard the integrity of healthcare services.
What is cybersecurity in healthcare?
Cybersecurity in healthcare refers to protecting electronic information – sensitive patient data, healthcare systems, and digital infrastructure – from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure. The 3 objectives of healthcare cybersecurity are the “CIA triad,” securing the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of healthcare information against breaches and malicious activities.
Cybersecurity demands implementing cutting-edge measures to
- prevent,
- detect, and
- respond
to cyber threats.
Cybersecurity in healthcare: understanding the stakes
The intersection of healthcare and technology has brought about numerous advancements, improving patient care and operational efficiency, such as using EHRs, telehealth, remote patient monitoring by hospitals and clinics, and IoT healthcare products by individual consumers. However, it has brought in new risks and vulnerabilities.
Healthcare organizations store vast amounts of sensitive data, including medical records, personal information, and financial details. This treasure trove of data makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals who seek to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or to cause disruption.
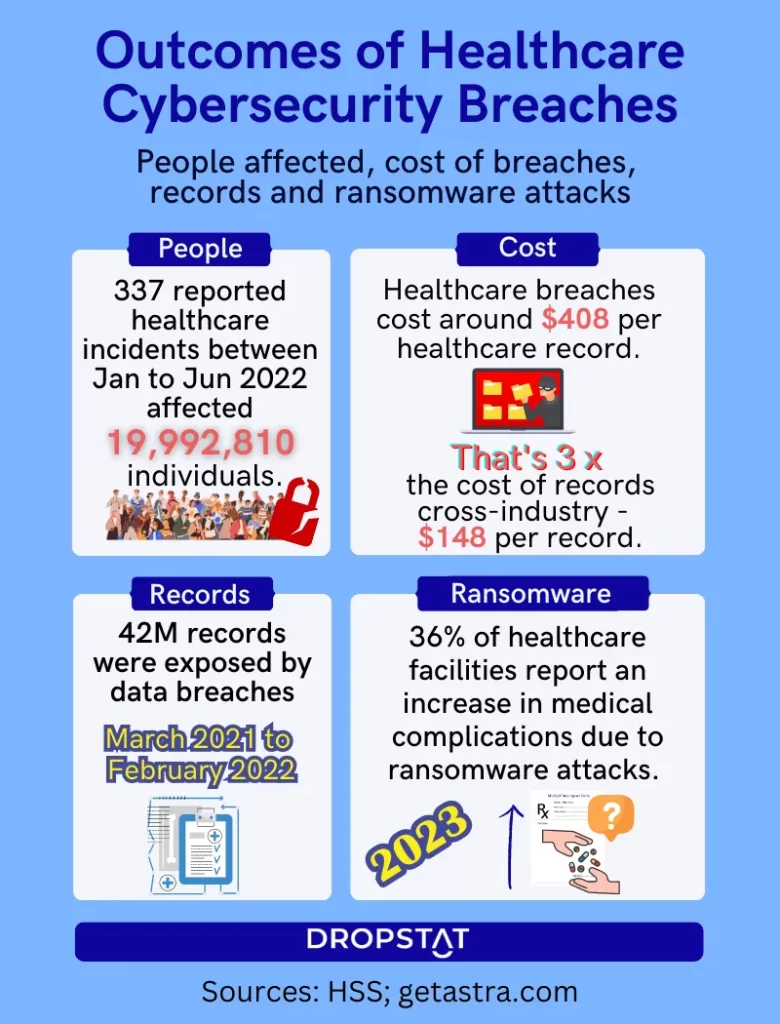
Healthcare cyber attacks are a growing threat
The intersection of healthcare and cybersecurity is crucial for ensuring the protection of patient information and maintaining the integrity of healthcare systems. However, the healthcare industry has witnessed a significant increase in cyber attacks in recent years. These attacks can have far-reaching consequences, threatening patient privacy, compromising clinical outcomes, and straining a hospital’s financial resources.
The highest cost of a data breach across industries is a data breach in healthcare. A single data breach event in healthcare can cost around $10.10 million. It can impact millions of people, exposing sensitive patient data, leading to identity theft, insurance fraud, or even blackmail.
Furthermore, the integrity of clinical data can be compromised, potentially impacting patient care and treatment decisions. The financial impact of responding to an attack means incurring costs for incident response, legal fees, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Why is cybersecurity more critical in healthcare?
Healthcare cybersecurity is more critical than cybersecurity in other industries due to several factors.
- Firstly, the healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the value and sensitivity of the data found in its records.
- Secondly, the increasing digitalization of healthcare systems and the adoption of electronic health records have expanded the attack surface and introduced new vulnerabilities.
- Thirdly, healthcare organizations must comply with stringent regulations, such as the HSS (Health and Human Services), which mandates the protection of patient health information. Failure to meet mandated requirements can result in severe consequences, including legal repercussions and damaged reputations.
Healthcare managers often struggle to keep up to date on healthcare cybersecurity and feel they are on the front line of attack. They want to adopt new protective technologies, but there are many stakeholders involved, which makes change management in healthcare more complex. Nevertheless, the healthcare industry is poised to protect itself from security breaches in healthcare, primarily through increasing awareness of cybersecurity challenges in healthcare.

The most significant types of cyber threats affecting healthcare
Let us review some significant varieties of cybersecurity issues in healthcare.
Ransomware attacks
Ransomware is a vicious and malicious type of software. It encrypts data on a computer system, rendering it inaccessible to the real owners until a ransom is paid. Healthcare organizations are often targeted due to the sensitive nature of patient data, and these attacks can disrupt critical operations and compromise patient care.
Phishing attacks
Phishing involves fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information from individuals or organizations – usually login credentials or financial details – by the attacker disguising himself as a trustworthy entity. Healthcare professionals may receive phishing emails that appear to be from reputable sources, leading them to disclose sensitive information or download malware unknowingly.
Insider threats
Insider threats are malicious activities perpetrated by individuals within an organization who have authorized access to systems and data. This can include employees, contractors, or even healthcare professionals. Insider threats can result in the theft, destruction, or unauthorized disclosure of sensitive data. Disclosure isn’t always initiated with malicious intent; it could stem from a lack of attention. Negligent employees cause 61% of healthcare data breach threats.
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks
In healthcare, DDoS attacks aim to overwhelm a target healthcare system or network with an influx of traffic, causing a disruption in service availability. This can lead to critical systems becoming inaccessible, hindering patient care and creating operational challenges.
Data breaches
Data breaches involve unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive patient information, such as medical records or personal details. These breaches can occur due to vulnerabilities in systems, weak security practices, or targeted attacks, and they pose significant risks to patient privacy and can result in identity theft or fraud.
Malware infections
Malware refers to malicious software that is designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Healthcare organizations can be targeted by various forms of malware, including viruses, worms, and Trojans, which can compromise the integrity of data and systems.
Social engineering attacks
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals to gain access to personal information or network systems. Dishonest tactics such as impersonation, deception, or psychological manipulation are common tools for such attacks. Healthcare professionals may be targeted through phone calls, emails, or in-person interactions.
IoT vulnerabilities
The Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as medical devices or wearable health trackers, are increasingly being used in healthcare. However, these devices can introduce vulnerabilities if not properly secured, potentially allowing unauthorized access to patient data or disrupting their functionality.
It is crucial for healthcare organizations to stay ahead of cyber threats and implement robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risks.
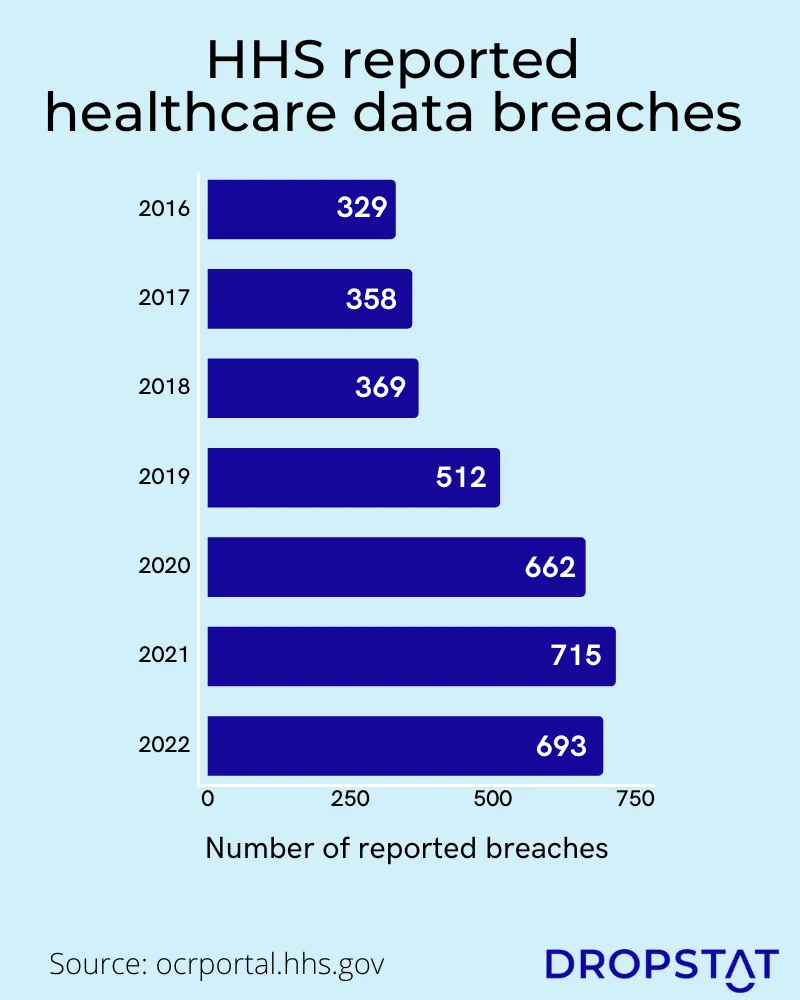
8 Ways to prevent data breaches and healthcare cyber attacks
Healthcare organizations must adopt proactive strategies to strengthen cybersecurity defenses and protect against data breaches and cyber-attacks. Here’s how to minimize cybersecurity challenges in healthcare
1. Enforce powerful security solutions and satisfy healthcare cybersecurity regulations
Invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions tailored to the healthcare industry as mandated by healthcare cybersecurity regulations and frameworks. These include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption tools, and endpoint protection software. Cybersecurity in healthcare is a requirement under
- The HIPAA Security Rule requires health plans, providers, clearing houses, and business associates to protect ePHI (electronically stored, protected health information).
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (the NIST cybersecurity framework) Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure; ISO/IEC 27001 mandates this for all federal agencies and contractors.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) must be upheld wherever an organization stores, processes, or transmits data about credit card holders.
- The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) – an organization that helps raise awareness of healthcare cybersecurity threats such as by publishing a list of known malware strains.
2. Conduct regular security assessments and prevent data breaches in healthcare
The chief information security officer (CISO) performs regular vulnerability assessments. The CISO or chief information officer (CIO) also conducts penetration testing to identify and addresses weaknesses in healthcare digital systems, networks, and applications. Professional cybersecurity assessments often prevent attempted fraud and healthcare data theft.
3. Educate and train employees in healthcare cybersecurity best practices
Build a culture of cybersecurity awareness by providing comprehensive training to employees at all levels. Teach them about common attack vectors – used in hacking healthcare sites, phishing techniques, and best practices for data protection when using healthcare technology.
4. Neutralize cybersecurity threats in healthcare with strong access controls
Implement strict access controls and least-privilege principles to make sure that authorized individuals are the only ones who can access sensitive data and systems. Limit security gaps by adopting privilege escalation when accessing healthcare networks.
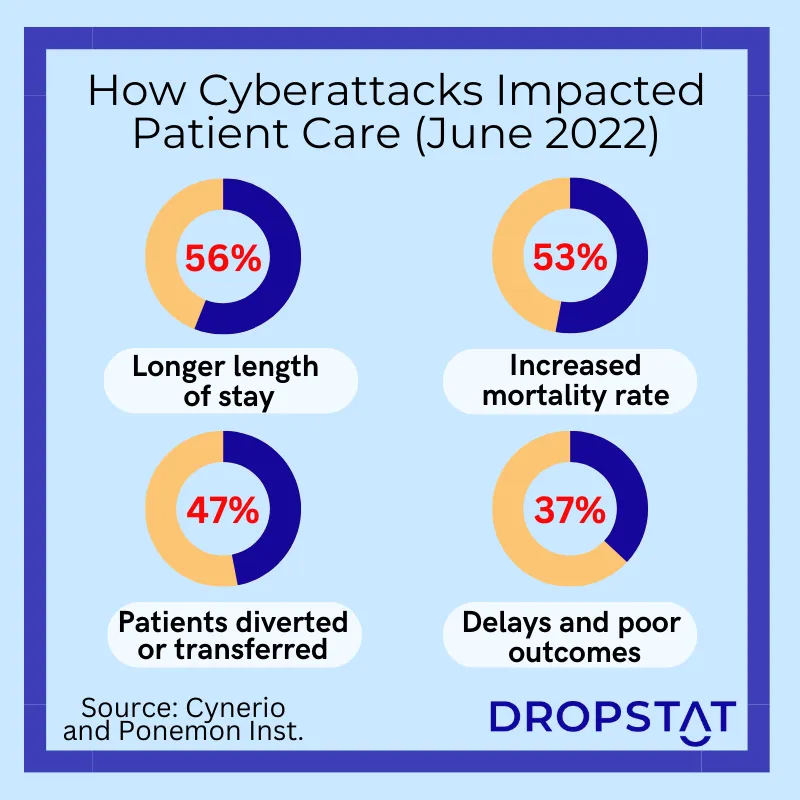
5. Develop an incident response plan to limit the effects of any healthcare hacking
Prepare for potential cyber incidents by developing an incident response plan. The plan should outline which steps to take in the case of a breach, including containment, investigation, notification, and recovery. Use cybersecurity professionals to identify legacy systems, apply health information technology, and design security strategies to tighten up digital health systems.
6. Avoid a healthcare cyber attack – get the latest patches and updates
Regularly apply patches and updates to apply the newest healthcare cybersecurity solutions to all software, including operating systems, applications, and security tools. These updates often address known vulnerabilities and can strengthen ongoing security measures.
7. Foster partnerships and share information to boost cybersecurity in healthcare
Collaborate with industry peers, cybersecurity experts, and government agencies to share information about emerging threats, best practices, and new security solutions. Many healthcare organizations and healthcare practitioners actually improve healthcare delivery as a result of partnerships that begin as a response to cyber risk, discovering that together is stronger in healthcare delivery.
8. The ultimate cybersecurity for healthcare is continuous monitoring and improvement
Establish a robust monitoring system to detect and respond to potential threats in actual time. Regularly review and enhance cybersecurity protocols based on emerging threats and industry trends.
By adopting proactive measures, healthcare organizations can significantly reduce the number of data breaches and cyber attacks on healthcare and enhance their cybersecurity posture. These should be top priorities for healthcare facility CEOs and leaders. Currently, healthcare cyber attack statistics show that, on average, healthcare facilities only invest between 4% and 7% of their IT budget in cybersecurity. This indicates existing security gaps between awareness of the dangers of healthcare cyberattacks and tackling the problem effectively.

What are cybersecurity trends in healthcare?
Cybersecurity trends in healthcare are the evolving patterns and developments in the field of cybersecurity specifically relevant to the healthcare industry. Some of the key trends include
- Increased focus on data privacy: Healthcare organizations are placing greater emphasis on data privacy, ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
- Adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) for cybersecurity: AI-powered technologies are being utilized to detect and respond to cyber threats more effectively.
- Integration of IoT security: The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in healthcare introduces new security challenges. Protecting networked medical devices and ensuring their secure integration into healthcare systems is a key trend in healthcare cybersecurity.
Application of healthcare cybersecurity trends
- Patient safety, protection of patient privacy and care delivery, and patient records.
- Preserving electronic PHIs (protected health information) and data from connected medical devices/mobile devices and medical systems benefit.
- Preventing security incidents, protecting financial information, and preserving the health facility’s integrity in the public eye.
Cybersecurity in healthcare and the threats to its smooth running will continue to develop. Healthcare organizations must continue to respond by protecting themselves, learning more, and being 100% aware of cyber threats via cybersecurity professionals. Through this, hospitals and healthcare facilities can enjoy the benefits of digital developments and the efficiency it brings while limiting the risk to the healthcare industry.
How Dropstat supports the secure functioning of healthcare organizations
Dropstat is an AI-powered staff scheduling app designed to help thriving healthcare organizations optimize staffing protocols. It is a safe way for healthcare facilities to communicate with nurses within a unit and within the facility. Dropstat’s functional design is secure and encrypted, as it has all the safety features required by U.S. regulatory bodies.
Schedule a demo with Dropstat and reveal how your facility can benefit from Dropstat’s safe and encrypted security system in the healthcare staffing arena.







